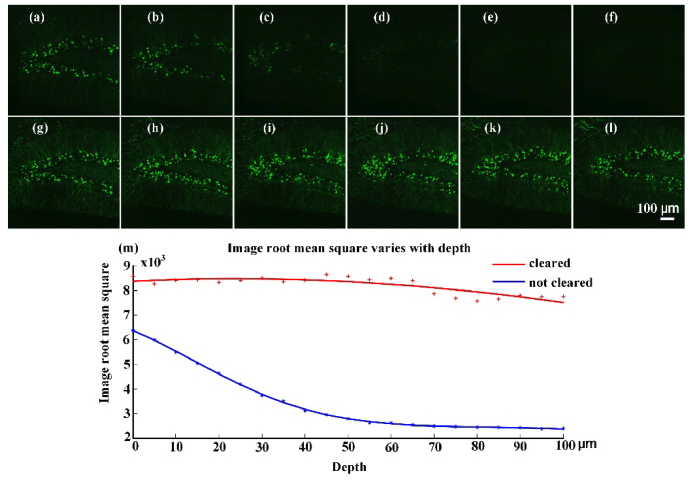
On-line optical clearing method for whole-brain imaging in mice
This new study by Wu and colleagues demonstrates that it is possible to clear an agar-embedded mouse brain during serial section imaging. Using a mixture of fructose and urea in PB, the authors were able to image deeper without loss of signal and without initial clearing of the whole organ. Clearing was demonstrated up to a depth of 100 microns. The approach speeds up imaging because fewer cuts needed and increases quality because signal intensity does not drop with depth. The technique introduces minimal brain deformation. The downside of the approach is that the clearing solution has a high refractive index (about 1.48) and so a water immersion objective will not be suitable. The approach is therefore best for situations where higher power oil immersion objectives are desirable. The authors’ detailed images show examples of clearing quality in gray matter, but not in harder to clear white matter.